Interpretable phenotype-aware models
PhenoSV: interpretable phenotype-aware model for the prioritization of genes affected by structural variants
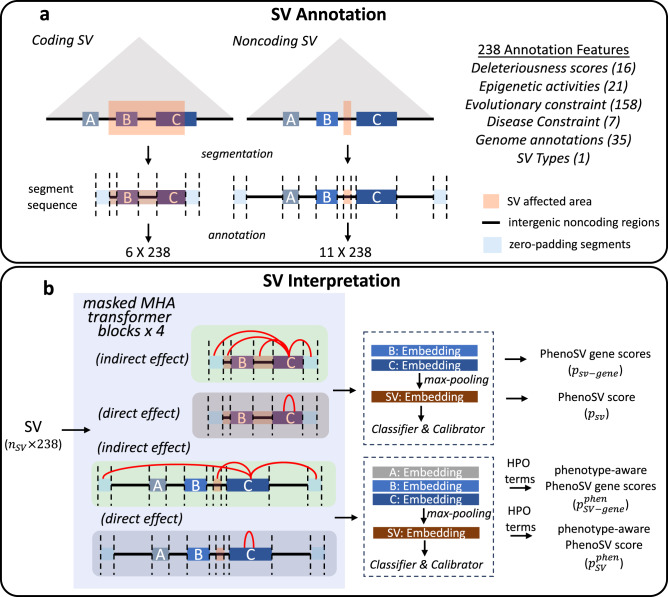
Structural variants (SVs) are a significant source of genetic variation linked to phenotypic diversity and disease risk. Although long-read sequencing technologies can identify over 20,000 SVs in a human genome, understanding their functional implications remains a challenge. Current methods for detecting disease-related SVs focus primarily on deletions and duplications, and they are unable to pinpoint specific genes impacted by SVs, particularly for noncoding variants. In this study, we introduce PhenoSV, a machine-learning model that incorporates phenotype information to interpret all major types of SVs and the genes they affect. PhenoSV segments and annotates SVs with a range of genomic features, using a transformer-based architecture within a multiple-instance learning framework to predict their potential effects. By leveraging gene-phenotype associations, PhenoSV can prioritize SVs related to specific phenotypes. Extensive evaluation on diverse human SV datasets demonstrates PhenoSV’s superior performance compared to other methods. When applied to disease studies, PhenoSV effectively identifies disease-associated genes affected by SVs. PhenoSV is accessible through both a web server and a command-line tool, available at https://phenosv.wglab.org.