Our paper on HDAC Inhibition
Genomic responses to HDAC inhibitors in prostate cancer cells
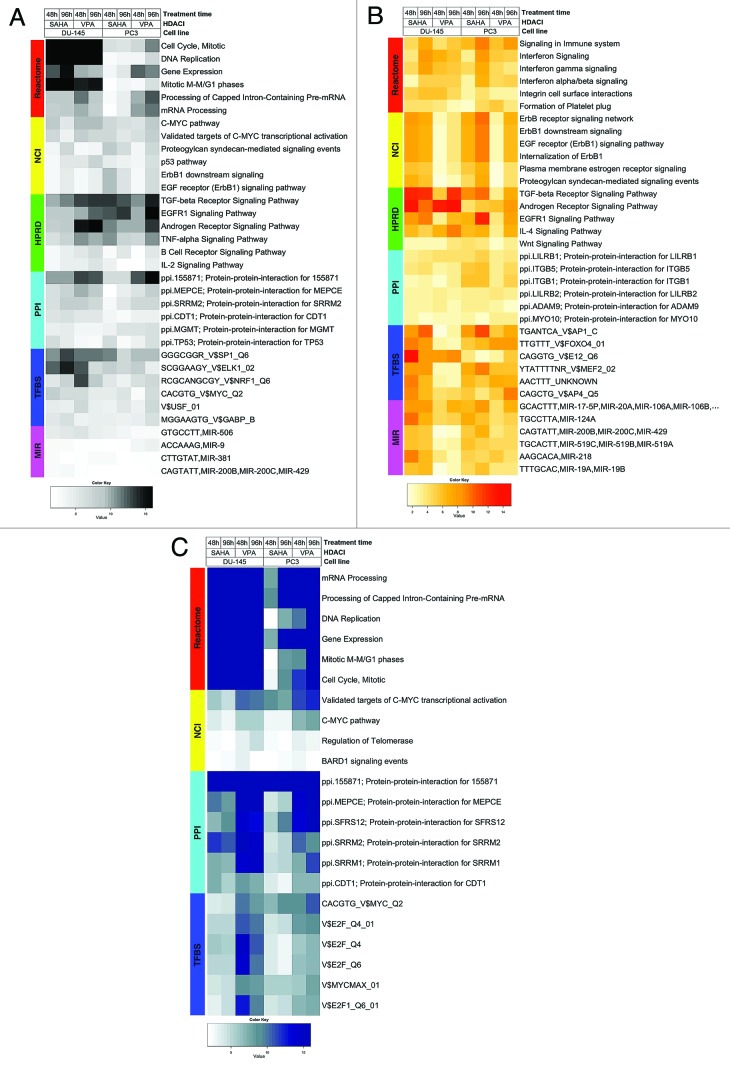
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) have become significant targets for cancer therapy. HDAC inhibitors (HDACis) are well tolerated by patients and have been approved for treating cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). To enhance the clinical benefits of HDACis in solid tumors, combination therapies involving HDACis may be considered. In this study, we used Analysis of Functional Annotation (AFA) to create a comprehensive list of genes and pathways affected by HDACi treatment in prostate cancer cells. This method provides an unbiased and objective way to analyze high-throughput data. By performing AFA on gene expression data from prostate cancer cell lines DU-145 (HDACi-sensitive) and PC3 (HDACi-resistant), treated with HDACis valproic acid or vorinostat, we identified biological processes altered by HDACis, suggesting potential targets for combination therapies. Our analysis revealed that HDAC inhibition led to, among other effects, upregulation of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes and disruption of the mitotic spindle checkpoint due to downregulation of mitosis-related genes. These findings were further validated through AFA on publicly available datasets of HDACi-treated prostate cancer cells. In total, we analyzed 375 microarrays from HDACi-treated and control prostate cancer cells. All results from this extensive analysis are made available as an online resource (accessible at the journal’s website and at http://marchionni.org/HDACIs.html). By publishing this data, we aim to improve the understanding of cellular changes following HDAC inhibition and identify new potential combination strategies for treating prostate cancer.
Here is our work on transcriptional responses to HDAC inhibitors in prostate cancer. Extensive supplementary material is also available here
Also, please visit this page for commentary on our manuscript